- Malad West, Mumbai
- +91-7400188399
- mccmumbaicosmeticcentre@gmail.com
Hypertrichosis Treatment
Hypertrichosis Treatment in Mumbai
What is Hypertrichosis?
Hypertrichosis is a rare condition characterized by excessive hair growth anywhere on the body beyond the age, sex, and race. It can affect both men and women, and while it's not life-threatening, it can significantly impact a person's self-esteem and quality of life.
Mumbai Cosmetic Centre provides Hypertrichosis treatments in Malad mumbai, addressing excessive hair growth for a smoother, more confident you. Book now!
Types of Hypertrichosis
This type is present at birth and is often linked to genetic factors.
2. Acquired HypertrichosisThis type develops later in life and can be triggered by medications, hormonal imbalances, or underlying medical conditions.

Causes of Hypertrichosis
The causes of hypertrichosis can vary depending on the type:
1. Congenital HypertrichosisThis form is primarily genetic, often inherited through a family's genes. It can be linked to specific genetic mutations that lead to abnormal hair growth patterns.
2. Acquired HypertrichosisAcquired hypertrichosis can result from several factors:
Medications:Some drugs, such as minoxidil (used for hair loss treatment), cyclosporine (an immunosuppressant), and phenytoin (an anticonvulsant), can cause excessive hair growth as a side effect.
Hormonal Imbalances:Medical condition like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can lead to hormonal imbalances that trigger hypertrichosis.
Malnutrition:Severe malnutrition, especially during childhood, can sometimes lead to hypertrichosis.
Cancer:Certain types of cancer, particularly those affecting hormone-producing glands, may cause hypertrichosis as a secondary symptom.
Diagnosis of Hypertrichosis
Diagnosing hypertrichosis typically involves a thorough medical history review, physical examination, and sometimes, additional tests. A cosmetologist or healthcare provider may ask about family history, medication use, and any associated symptoms. They may also perform blood tests to check hormone levels and rule out underlying medical conditions.
In cases where hypertrichosis is suspected due to medication use or a specific medical condition, discontinuing the medication or treating the underlying cause may lead to a reduction in hair growth.
Prevention of Hypertrichosis
Preventing hypertrichosis largely depends on the underlying cause:
Genetic Hypertrichosis:Since congenital hypertrichosis is genetic, it's challenging to prevent. Genetic counseling can be useful for families with a history of the condition.
Medication-Induced Hypertrichosis:If taking medications known to cause hypertrichosis, discussing alternative treatments with a healthcare provider may be an option.
Hormonal Imbalances:Managing underlying conditions like PCOS or adrenal disorders through medication and lifestyle changes can help prevent hormonal-related hypertrichosis.
Healthy Lifestyle:Following a balanced diet, regular exercise, and managing stress can help to maintain overall well-being and may indirectly help prevent certain forms of hypertrichosis.
Top Hypertrichosis Experts in Mumbai
FAQs
1. What are the main symptoms of hypertrichosis?
Hypertrichosis is characterized by excessive hair growth beyond what is considered normal for age, sex, and race. The symptoms include thick and dark hair growth on areas of the body where hair is not typically found in large amounts, such as the face, back, shoulders, and limbs.
2. Can hypertrichosis be treated permanently?
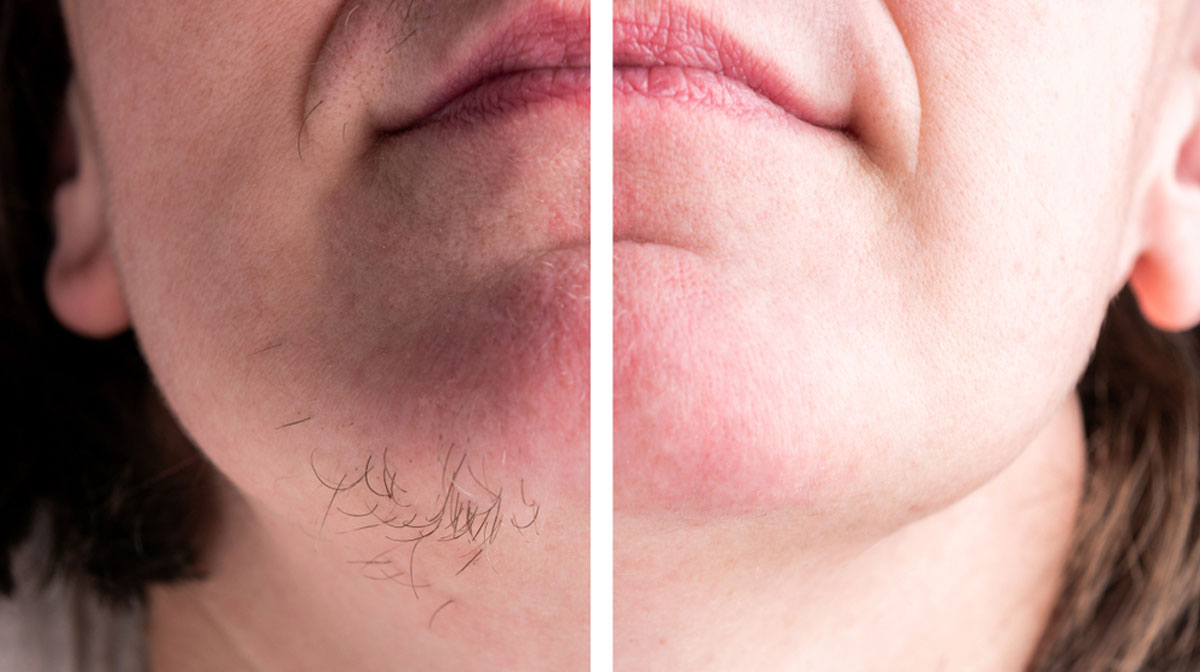
While there is no cure for hypertrichosis, there are treatments available to manage excessive hair growth. Methods like laser hair removal and electrolysis can provide long-lasting or permanent reduction in hair growth in affected areas.
3. What are the most common treatment options for hypertrichosis?
Treatment options for hypertrichosis include hair removal methods such as shaving, waxing, laser hair removal, and electrolysis. Creams to reduce the hair growth is also suggested.