- Malad West, Mumbai
- +91-7400188399
- mccmumbaicosmeticcentre@gmail.com
Pigmentation Treatments
Pigmentation Treatment In Mumbai
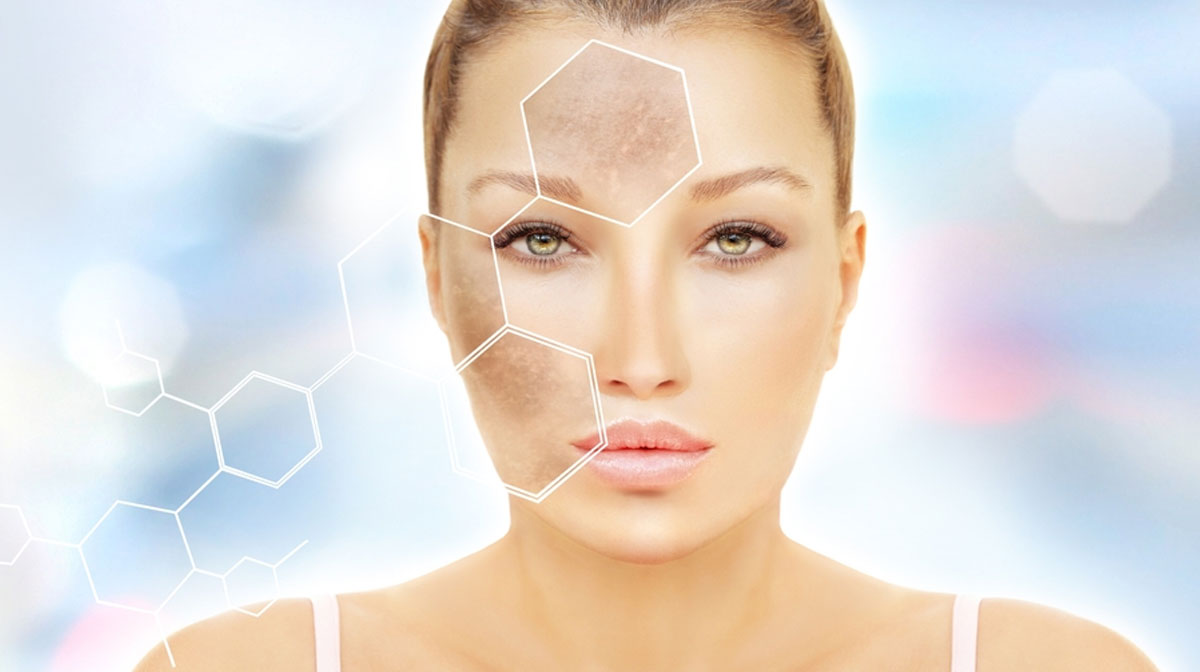

What is Pigmentation?
Pigmentation refers to the coloring of the skin, hair, and eyes. It occurs due to the presence of melanin, a pigment produced by melanocytes in the skin. Melanin plays a crucial role in protecting the skin from the harmful effects of UV radiation. But sometimes various factors can lead to abnormal pigmentation, causing skin discoloration and other aesthetic concerns.
Mumbai Cosmetic Centre offers specialized treatments for pigmentation in Malad Mumbai, helping you achieve clearer, more even-toned skin with expert care.
Types of Pigmentation
1. Hyperpigmentation:It is darkening of the specific area of the skin compared to the surrounding area. It can be caused by excess melanin production, hormonal changes, sun exposure, inflammation, or certain medications. Common forms of hyperpigmentation include melasma, post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, and age spots.
2. Hypopigmentation:This condition leads to lighter patches of skin due to reduced melanin production or distribution. Conditions like vitiligo, albinism, and certain fungal infections can cause hypopigmentation.
Causes of Pigmentation Disorders
Sun Exposure:UV radiation can stimulate the production of more melanin, leading to tanning or sunspots.
Hormonal Changes:Pregnancy, hormonal contraceptives, and hormonal imbalances can trigger melasma.
Inflammation:Acne, eczema, and other inflammatory skin conditions can cause post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
Genetics:Certain genetic conditions like albinism can result in hypopigmentation.
Medications:Certain antibiotics and chemotherapy drugs, can cause pigmentation changes as a side effect.
Age:As people age, they may develop age spots or lentigines due to cumulative sun exposure over time.
Diagnosis of Pigmentation Disorders:
To diagnose pigmentation disorders, cosmetologist typically perform a thorough examination of the skin and may use additional tools such as:
Skin Biopsy:In some cases, a skin sample may be taken for microscopic examination to determine the cause of pigmentation changes.
Blood Tests:If hormonal imbalances are suspected, blood tests may be suggested to assess hormone levels.
Prevention of Pigmentation Disorders
While some pigmentation changes are inevitable, several preventive measures can help minimize their occurrence:
Sun Protection:Always wear sunscreen with a SPF 30 or above, wear protective clothing, and seek shade during peak sun hours.
Avoid Hormonal Triggers:If you're prone to melasma, discuss alternative contraceptives or hormonal therapies with your healthcare provider.
Manage Inflammation:Treat inflammatory skin conditions promptly to reduce the risk of post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
Healthy Lifestyle:Maintain a balanced diet, stay hydrated, and avoid smoking, which can contribute to premature skin aging and pigmentation issues.



Pigmentation disorders are common skin concerns that can affect individuals of all ages and skin types. Consulting a cosmetologist for personalized evaluation and treatment recommendations is key to managing pigmentation disorders successfully.
Top Pigmentation Experts in Mumbai
FAQs
1. Can pigmentation disorders be cured completely?
While some pigmentation disorders can be effectively managed and improved, complete cure may not always be possible, especially for conditions like vitiligo.
2. Are over-the-counter (OTC) products effective for treating pigmentation?
Some OTC products containing ingredients like vitamin C, niacinamide, and licorice extract may help with mild pigmentation issues. However, for more significant concerns, prescription-strength treatments may be necessary.
3. Is it safe to use home remedies for pigmentation?
Certain home remedies like lemon juice or apple cider vinegar may be popular, but they can also cause skin irritation and worsen pigmentation in some individuals. It's best to consult a cosmetologist before trying home remedies.
4. Can pigmentation disorders affect mental health?
Yes, pigmentation disorders, especially those that are highly visible or cause significant changes in appearance, can impact self-esteem and mental well-being. Seeking support from a cosmetologist or mental health professional can be beneficial.
How long does it take to see results from pigmentation treatments?
The timeline for seeing results varies depending on the treatment used, the severity of pigmentation, and individual factors. Some treatments may show improvement within weeks, while others may require several sessions over months for noticeable changes.