- Malad West, Mumbai
- +91-7400188399
- mccmumbaicosmeticcentre@gmail.com
Acne Scars Treatment
Acne Scars Treatment In Mumbai
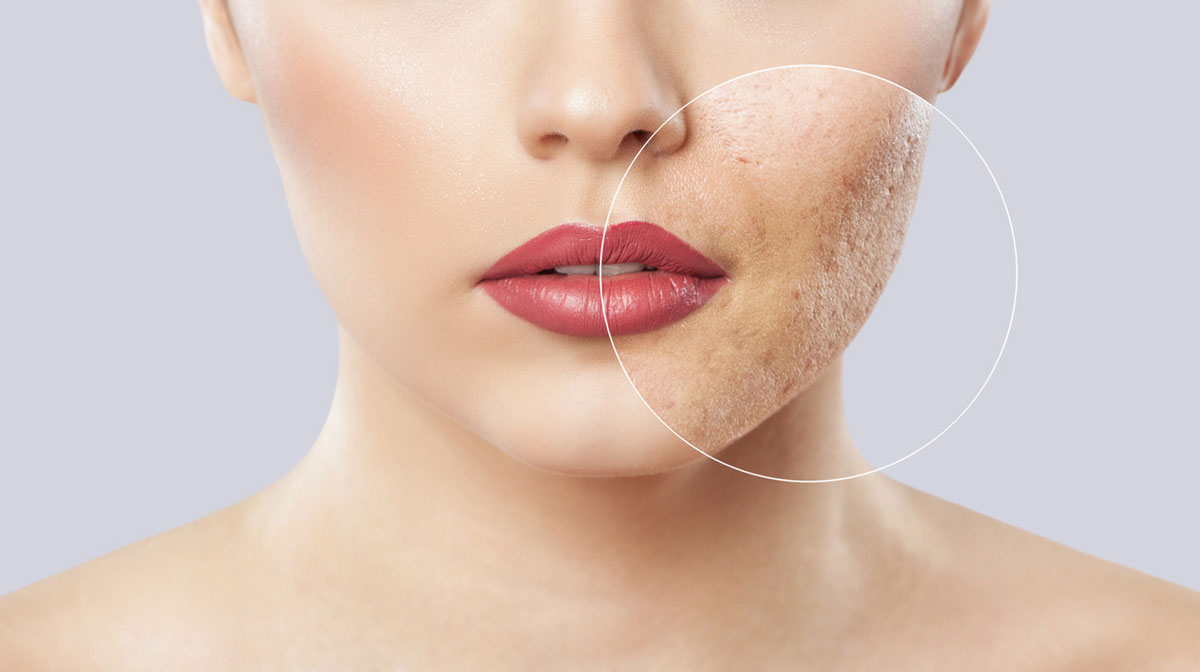

What are Acne Scars?
Acne scars are permanent textural changes and marks on the skin that occur as a result of severe acne lesions. These scars can be seen in various forms, including depressions or pits, raised areas, and discoloration. They often develop when the skin's normal healing process is disrupted during severe acne outbreaks, leading to abnormal collagen production and tissue damage.
Mumbai Cosmetic Centre offers advanced acne scar treatments in Malad Mumbai, restoring smooth, blemish-free skin with expert care. Book your consultation now!
Types of Acne Scars
1. Ice Pick ScarsThese are deep, narrow scars that resemble small holes or pits on the skin's surface. They are often the result of deep acne lesions that damage the skin's deeper layers.
2. Boxcar ScarsBoxcar scars are broader depressions with defined edges and sides that make them look like a box. They typically occur due to inflammatory acne and are more common on the cheeks and temples.
3. Rolling ScarsRolling scars have a wavy or irregular texture and are caused by the tethering of the skin's underlying structures. They are often associated with inflammatory acne that affects deeper layers of the skin.
4. Keloid or Hypertrophic ScarsThese scars result from an overproduction of collagen during the healing process, leading to raised, thickened areas of skin. They are more common in individuals with a genetic predisposition to keloid formation.
5. Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH)While not technically scars, PIH refers to dark spots or discoloration left behind after acne lesions heal. They can persist for months or even years after the acne has resolved.
Causes of Acne Scars
Acne scars develop when acne lesions, particularly severe or cystic ones, damage the skin's collagen and elastin fibers. The body's attempt to repair this damage can result in the formation of scars. Factors that contribute to acne scarring include:
Inflammation:Severe in acne lesions can lead to tissue damage and scarring.
Genetics:Some people are genetically prone to developing more severe acne and subsequent scarring.
Delay in Treatment:Not seeking timely and appropriate treatment for acne can increase the risk of scarring.
Picking or Squeezing Acne Lesions:Picking acne can make the inflammation worse and increase the likelihood of scarring.
Diagnosis of Acne Scars
Cosmetologist typically diagnose acne scars based on an external visual examination of the skin and a review of the patient's medical history. They may also use tools such as a Wood's lamp or skin surface magnification to assess the severity and type of scarring. In some cases, a skin biopsy may be performed to rule out other skin conditions or assess the depth of scarring.




Prevention of Acne Scars
Some of the preventive measures you can take to reduce the acne scars are given below:
Early Treatment:Seek treatment for acne early to prevent severe acne that is more likely to scar.
Avoid Picking or Squeezing:Refrain from picking or squeezing acne lesions, as this can worsen inflammation and lead to scarring.
Gentle Skincare:Use gentle skincare products suitable for your skin type to avoid irritation and inflammation.
Sun Protection:Always protect your skin from sun exposure by using sunscreen daily, as UV rays can worsen hyperpigmentation and delay healing.